Important teaching points: (updated 12/20/18)
1) In patients with significantly elevated LFTs where there is even a concern for Tylenol induced injury, start NAC immediately. It can always be stopped and is well tolerated. Additionally, in non-acetaminophen cases of acute liver failure (see definition below) NAC has been shown to have benefit.
2) Always recheck toxin screens even if an outside hospital gives verbal report of their values, if there is no paper copy you must verify.
3) Remember LDH can be useful in work up of acute hepatitis, it will be elevated in early acute hepatitis and ischemic hepatitis (often markedly elevated in ischemic hepatitis). Though recall it is found in a variety of tissues and many processes can cause it’s elevation.
We heard a case of a young female with chronic abdominal pain presenting with 2 days of new abdominal pain and emesis she reported was very different from her usual. Her exam was remarkable for mild scleral icterus and diffuse abdominal pain without HSM, no skin or joint findings, no asterixis or stigmata of chronic liver disease and no LAD. She was transferred to UIHC from an OSH due to Tbili 3.6, ALT 1600 and AST 3700, on arrival at UIHC her Tbili was 3.0, ALT 3500 and AST 16000 with INR 2.2.
Remember, there are very few things that can give you elevated liver enzymes to this degree, a general guideline can be found here:

This table summarizes what we already talked about, which is that AST/ALT > 1000 should have a specific differential compared to more doest elevations
Others:
Mild-moderate elevation: malignant infiltration, muscle disorders, thyroid disorders, celiac disease, adrenal insufficiency, anorexia
Marked elevation: sinusoidal obstruction syndrome, HELLP, malignancy infiltration, toxin exposure (mushroom poisoning), heat stroke, sepsis
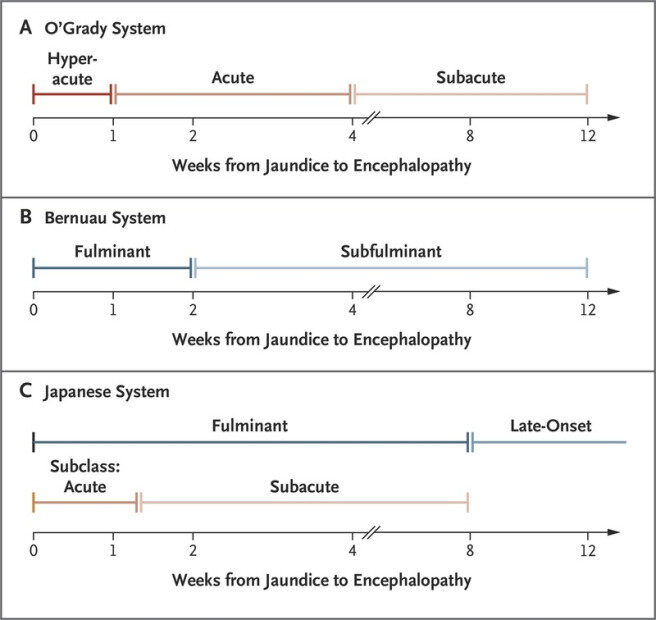
Also remember, acute liver failure is defined by length of time, requires synthetic dysfunction as evidenced by elevated INR and requires encephalopathy:
Case Conference 10.08.2018
APRIL 2, 2019 ~ INTMEDRESUIOWAEDU ~ EDIT”CASE CONFERENCE 10.08.2018″
At this lecture we discussed a 35 year old female with suspected GERD presenting with worsening epigastric pain and found to have elevated LFTs to >1000 (transaminases). She was diagnosed with drug induced liver injury secondary to (likely) nitrofurantoin and improved with steroids.
CaseConference10.08.2018
